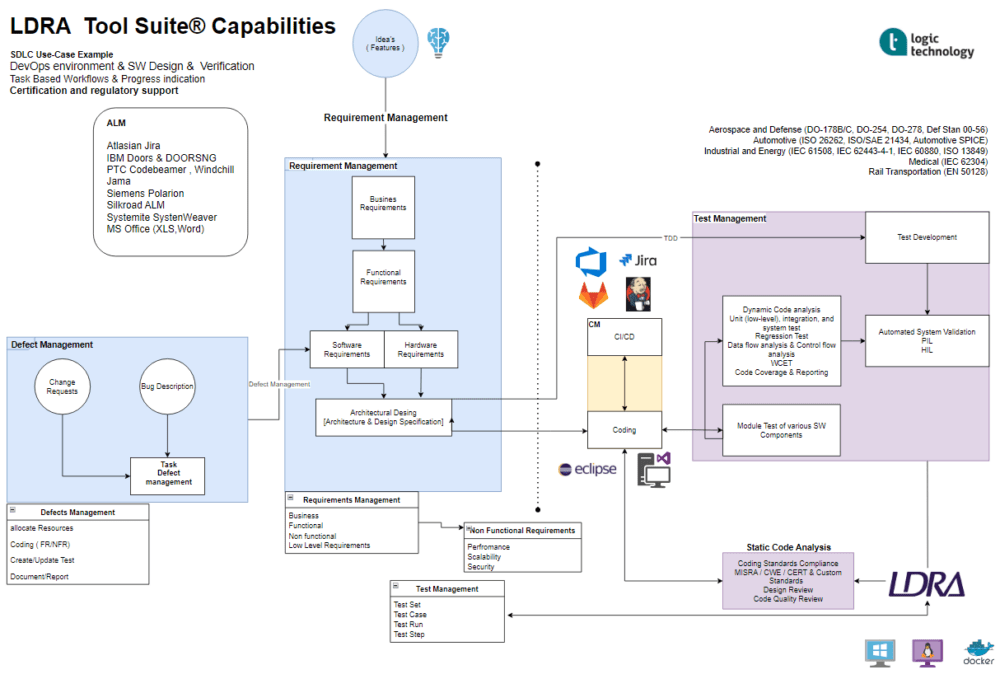
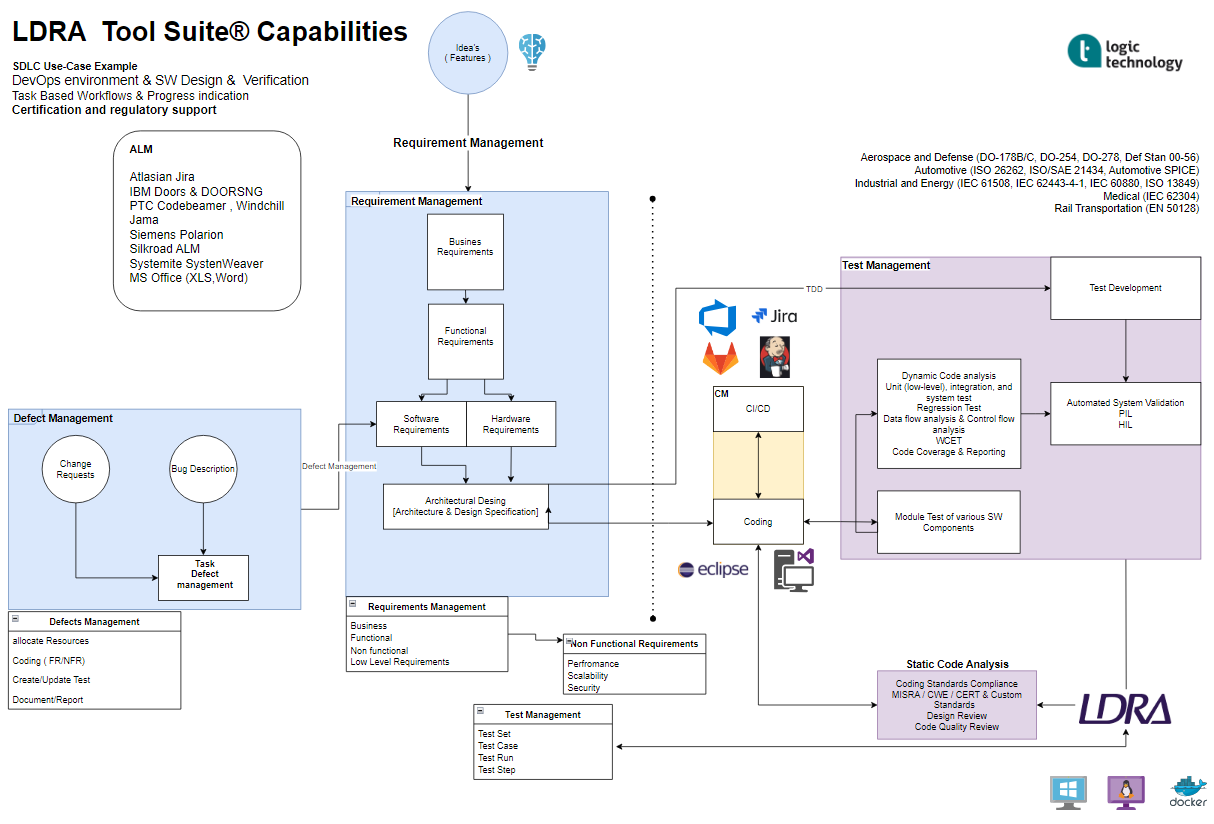
The software development process for embedded C/C++ programming typically follows a structured approach to ensure the quality, reliability, and efficiency of the final product.
Our brands

Our brands

Related articles

PRESS RELEASE – Logic Technology Appointed European Distributor for Lattix by CodeClinic
North Reading, MA United States & Beek (L), The Netherlands — July 29, 2025 CodeClinic LLC, a global provider of software quality and security solutions, is proud to announce the...
Read more
LDRA Joins Renesas Ready Partner Network and R-Car Consortium to Accelerate Safety-Critical Software Development, Verification and Certification
Read more
Cyber Resilience Act Compliance Guide
Read more
The Critical Need for Tracing in Real-Time Embedded Systems
Read more
Whitepaper – Effective power interruption testing – how best to fail
Read more
Software Development Process for Embedded C/C++ Programming
The software development process for embedded C/C++ programming typically follows a structured approach to ensure the quality, reliability, and efficiency of the final product. Here's a breakdown of the key activities involved:
- Requirements Analysis and Specification:
• Define System Requirements: Clearly outline the functional and non-functional requirements of the embedded system.
• Create Software Requirements Specification (SRS): Document detailed specifications for the software components, including input/output, performance, and memory constraints. - System Design:
• Architectural Design: Design the overall system architecture, breaking down the system into modules and components.
• Detailed Design: Design the detailed implementation of each module, including data structures, algorithms, and interfaces.
• Hardware/Software Partitioning: Determine how the functionality will be divided between hardware and software components. - Software Development:
• Coding: Write the C/C++ code based on the detailed design specifications.
• Coding Standards: Adhere to coding standards and guidelines to ensure code readability, maintainability, and portability.
• Modular Design: Break down the code into modular components for better organization and reusability.
- Software Testing:
• Unit Testing: Test individual functions and modules to verify their correctness.
• Integration Testing: Test the interaction between different modules to ensure they work together as expected.
• System Testing: Test the entire system to verify that it meets all functional and non-functional requirements.
• Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Testing: Simulate the hardware environment to test the software's interaction with the hardware. - Software Integration:
• Integrate Software with Hardware: Combine the software components with the hardware platform.
• Configure Hardware: Configure the hardware settings, such as clock speeds, memory mapping, and peripherals. - Software Verification and Validation:
• Verification: Ensure that the software meets its specified requirements.
• Validation: Ensure that the software meets the user's needs and expectations. - Software Deployment:
• Build and Link: Compile and link the code to generate executable code.
• Deploy to Target Hardware: Transfer the executable code to the target hardware. - Software Maintenance:
• Bug Fixes: Identify and fix any defects or errors in the software.
• Enhancements: Add new features or improve existing functionality.
• Configuration Management: Manage software versions and changes.
Additional Considerations for Embedded Systems
- Real-Time Constraints: Ensure that the software meets strict timing requirements.
- Resource Constraints: Optimize the software to use minimal memory and CPU resources.
- Power Consumption: Consider power consumption and energy efficiency.
- Security: Implement security measures to protect the system from attacks.
- Reliability: Design the software to be reliable and fault-tolerant.
By following these steps and considering the unique challenges of embedded systems, you can develop high-quality, efficient, and reliable embedded software.
LDRA Tool Suite
The LDRA tool suite is a flexible platform for producing safety, security, and mission-critical software in an accelerated, cost effective and requirements driven process.

Software Quality is a Team Responsibility
Let us help you optimizing your software development processes
Take the first step