Software Quality Tools
The software development process for embedded C/C++ programming typically follows a structured approach to ensure the quality, reliability, and efficiency of the final product.
Our brands

Our brands

Related articles

LDRA Joins Renesas Ready Partner Network and R-Car Consortium to Accelerate Safety-Critical Software Development, Verification and Certification
Expanded functional safety and security support enables comprehensive software verification across Renesas SoCs, MPUs and MCUs for applications in automotive, industrial, energy, medical and rail transportation. Wirral, UK—June 4, 2025—LDRA,...
Read more
Cyber Resilience Act Compliance Guide
Read more
The Critical Need for Tracing in Real-Time Embedded Systems
Read more
Whitepaper – Effective power interruption testing – how best to fail
Read more
Automated Test Case Generation in a Requirements-based testing process
Read more
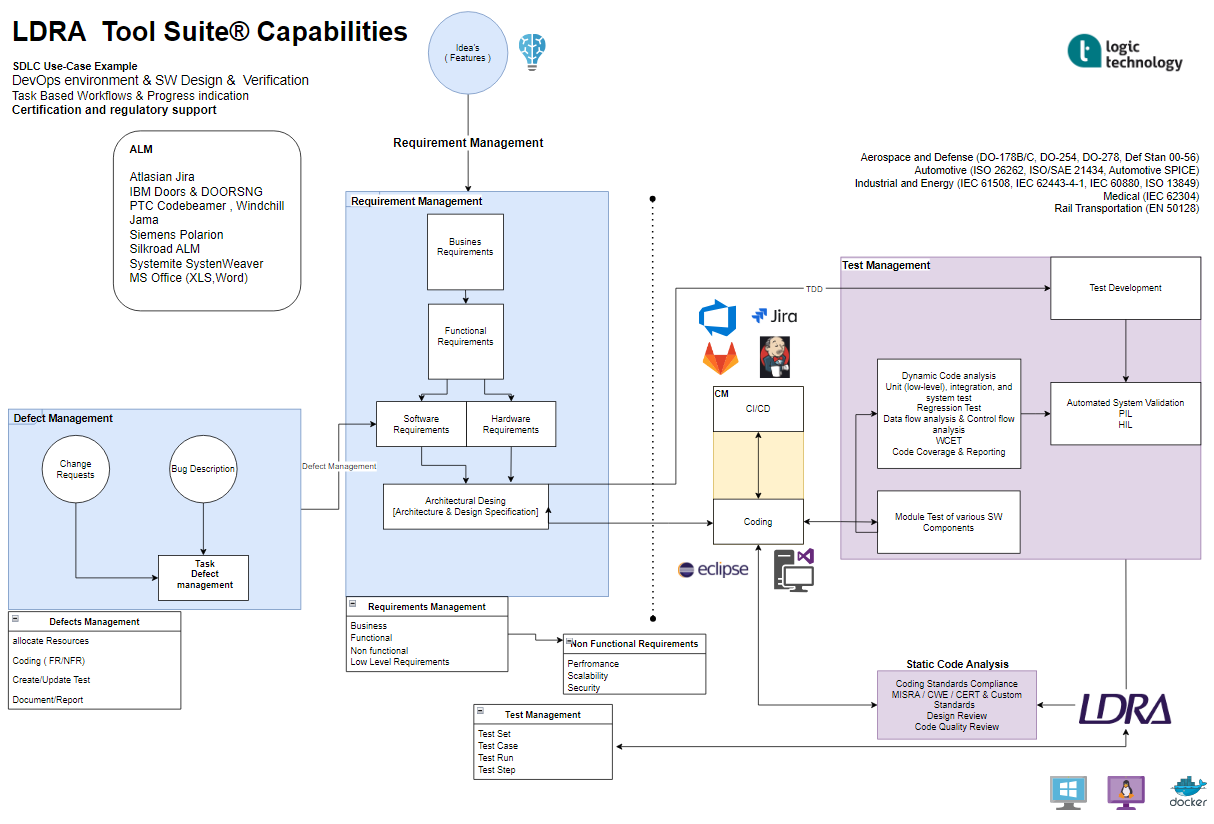
Software Development Process for Embedded C/C++ Programming
The software development process for embedded C/C++ programming typically follows a structured approach to ensure the quality, reliability, and efficiency of the final product. Here's a breakdown of the key activities involved:
- Requirements Analysis and Specification:
• Define System Requirements: Clearly outline the functional and non-functional requirements of the embedded system.
• Create Software Requirements Specification (SRS): Document detailed specifications for the software components, including input/output, performance, and memory constraints. - System Design:
• Architectural Design: Design the overall system architecture, breaking down the system into modules and components.
• Detailed Design: Design the detailed implementation of each module, including data structures, algorithms, and interfaces.
• Hardware/Software Partitioning: Determine how the functionality will be divided between hardware and software components. - Software Development:
• Coding: Write the C/C++ code based on the detailed design specifications.
• Coding Standards: Adhere to coding standards and guidelines to ensure code readability, maintainability, and portability.
• Modular Design: Break down the code into modular components for better organization and reusability.
- Software Testing:
• Unit Testing: Test individual functions and modules to verify their correctness.
• Integration Testing: Test the interaction between different modules to ensure they work together as expected.
• System Testing: Test the entire system to verify that it meets all functional and non-functional requirements.
• Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Testing: Simulate the hardware environment to test the software's interaction with the hardware. - Software Integration:
• Integrate Software with Hardware: Combine the software components with the hardware platform.
• Configure Hardware: Configure the hardware settings, such as clock speeds, memory mapping, and peripherals. - Software Verification and Validation:
• Verification: Ensure that the software meets its specified requirements.
• Validation: Ensure that the software meets the user's needs and expectations. - Software Deployment:
• Build and Link: Compile and link the code to generate executable code.
• Deploy to Target Hardware: Transfer the executable code to the target hardware. - Software Maintenance:
• Bug Fixes: Identify and fix any defects or errors in the software.
• Enhancements: Add new features or improve existing functionality.
• Configuration Management: Manage software versions and changes.
Additional Considerations for Embedded Systems
- Real-Time Constraints: Ensure that the software meets strict timing requirements.
- Resource Constraints: Optimize the software to use minimal memory and CPU resources.
- Power Consumption: Consider power consumption and energy efficiency.
- Security: Implement security measures to protect the system from attacks.
- Reliability: Design the software to be reliable and fault-tolerant.
By following these steps and considering the unique challenges of embedded systems, you can develop high-quality, efficient, and reliable embedded software.
LDRA Tool Suite
The LDRA tool suite is a flexible platform for producing safety, security, and mission-critical software in an accelerated, cost effective and requirements driven process.
Software Quality is a Team Responsibility
Let us help you optimizing your software development processes
Take the first step